Data Storage FAQ
API
Is there any limit to the number of API calls?
With Developer Edition, there is a free quota of 30,000 API read and write requests per day.
Push service is free to use, and does not take up the free quota. The call frequency of the push message interface is limited. For details, please refer to: Push message interface limitations documentation.
By default, the maximum number of worker threads that can be used by the Business Edition application at one time is 60, which means that at most 60 data requests can be processed at the same time. We will adjust this value based on application performance and operation and maintenance needs. If you need to increase this limit, please submit a work order to request it.
Calculation of the number of API calls
For data storage, each create and update of an object counts as 1 request, e.g. 1 call to object.saveInBackground counts as 1 API request. In the case of API call failure, if it is rejected by the cloud due to application flow control overrun (error code 429), it will not be counted as 1 request; if it is due to other reasons, for example, insufficient privileges (error code 430), it will still be counted as 1 request.
One request
createsavefetchfinddeletedeleteAll
A call to fetch or find that returns 100 associated objects via include counts as 1 API request. A call to find or deleteAll to find or delete 500 records counts as 1 API request.
Multiple requests
saveAllfetchAll
Calling saveAll or fetchAll once to save or fetch 100 objects in an array counts as 100 API requests.
For Social Stream, create and update are billed according to the number of objects in Status and Follower/Followee.
A query is billed by the number of requests, regardless of the size of the result. The query.count counts as 1 API request. Collection fetch is also billed by request count.
How to get API access logs
Go to Dashboard > Data Storage > API Access Logs, turn on the logging service, and refresh the page later to see the logs generated from the time it was turned on to the current time.
How to encode parameters for calling REST APIs in other languages
The REST API documentation uses curl as an example, where --data-urlencode indicates that the parameters are to be URL encoded.
In the case of a GET request, the URL encoded parameters are concatenated with & and placed after the question mark in the URL. For example, https://API_BASE_URL/1.1/login?username=xxxx&password=xxxxx.
Queries
How to implement case-insensitive queries
Direct support is not currently provided, a regular expression query approach can be used, see StackOverflow - MongoDB: Is it possible to make a case-insensitive query.
Use the matchesRegex method provided by the AVQuery object of each platform's SDK (Android SDK uses the whereMatches method).
What is the maximum number of results a query can return?
- A query can return up to 1000 pieces of data.
- If more than one query result is returned, the total size will not exceed 6 MB (for compatibility with old clients, if it exceeds 6 MB, no error will be reported and truncated results will be returned); if one query result is returned, the size will not exceed 16 MB.
The query result can only return 1000 pieces of data at most, what should I do when I need more than 1000 pieces of data?
You can continue to obtain new results from the previous breakpoint by changing the query conditions each time, for example:
- The first query, 1000 pieces of data whose createdAt time is after 2015-12-01 00:00:00 (the createdAt value of the last piece is x);
- The second query, createdAt is 1000 pieces of data after x (createdAt of the last piece is y);
- The third query, createdAt 1000 data pieces of data after y (the last piece is z);
And so on.
Can paging be accomplished by specifying a range of objectId's?
The current algorithm for automatically generating objectId by the datastore service is time-based, so paging can indeed be achieved by specifying theobjectId range.
However, from the perspective of code readability and rigor (e.g., you can specify different formats of objectId when importing data), it is recommended to implement paging by specifying the createdAt range.
How to speed up queries when the amount of data is increasing?
As with the use of traditional databases, query optimization is achieved primarily by indexing. An index is like a table of contents in a dictionary, which can help you look up words more quickly in a huge amount of text.
Principle: When the amount of data is small, no index is built. When there is more, please remember that after building an index, you still need to update the index when writing, in exchange for less query time. Therefore, in general, if you write less and read more, you can build more indexes; if you write more and read less, you can build less indexes.
Indexes can be created in Dashboard > Data Storage by selecting the corresponding Class and going to "Performance and Indexing" self-service, see console guide for more details. index).
Does LeanCloud query support functions like Sum, Group By, Distinct?
No. 'Group By] queries often involve traversing a large number of objects, and data storage is not suitable for such scenarios. For this reason we recommend using the "data warehouse" feature, which supports large and efficient data traversal, tailored for data analysis as a scenario.
Why query results for default values are incorrect?
This is the limitation of default value. MongoDB itself does not support default values. The default value we provide is only the enhancement of the application level. If the old data does not have a corresponding key, it will not be corrected after setting the default value, but the presentation layer will be optimized after querying. Accordingly, after changing the default value, these keys will also be displayed as the new default value. There are two solutions:
- Update the old data, query the records where the key does not exist (whereDoesNotExist), and then update them back.
- Add or query to the query condition, or key does not exist (whereDoesNotExist).
How do I query for non-null values?
The specific semantics of a null value depends on the type of the field and the actual situation of the item. Taking a string field as an example, a null value might mean:
- the field does not exist
- the field is `null'
- the field is the empty string
"".
Accordingly, the query for the field being non-null is where={"some_field": {"$exists": true, "$nin": ["", null]}}.
Determining a rigorous specification during the data model design phase of a project can help simplify query conditions and avoid errors due to inadvertent omission of conditions.
For example, if the design ensures that a string field is empty by simply not setting the field (it doesn't exist) and never setting it to "" and null (setting a field to null is strongly discouraged, the SDK doesn't provide a way to set a field to null), then simply querying for {"$exists": true} would be sufficient.
Geolocation query error
If the error message is similar to can't find any special indices: 2d (needs index), 2dsphere (needs index), for field name, it means that the field used for the query doesn't have a 2D index, you can find Indexes management in the Other menu of the Class management. You can find Index Management in the Other menu of Class Management, click to enter, find the field name, select and create "2dsphere" index type.
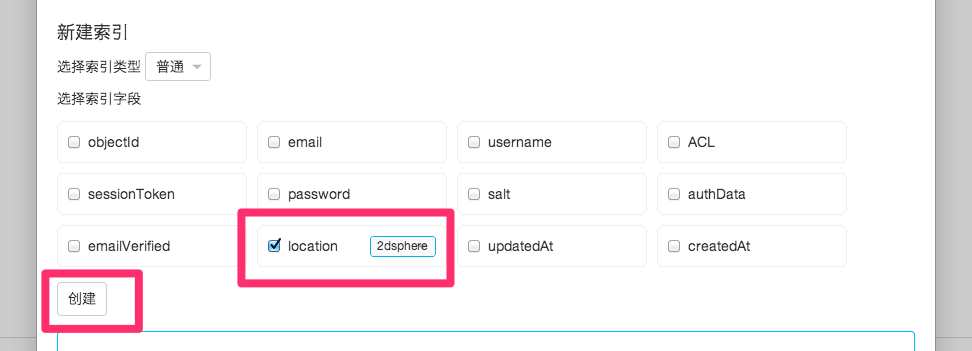
How to improve query efficiency of flag bits?
When there are many Boolean types of data in the data table, you can consider using binary storage to improve the query efficiency. For example, if you need to store multiple states such as whether push is enabled, whether you are muted,whether you are a member, etc., you can represent it like this:
111: Turn on push, mute, and be a member
101: Turn on push, not muted, and be a member
Stored as an integer field in LeanCloud, the method to manipulate this field can be found in the interface documentation for bitwise operations: REST API - Bitwise Operations.
When searching for keywords in the app, the result is data from two months ago. What should I do if the latesxt data cannot be queried?
In this case, you can try to rebuild the index in Dashboard > Data Storage > Full text search , and there will be a reminder by email after the index is created.
Generally speaking, when a user uploads a new dictionary, or deletes data in a batch, it is necessary to perform a "rebuild index" operation. You can also try to rebuild the index when you find inconsistencies between searches and stored data.
What should I do if a single object in a table is too large, resulting in slower requests?
If the data of a single object is too big, you need to optimize the code at the business level, for example, data is a big data field:
- When querying, use AVQuery.Select to select the required field (don't select data field).
- Fetch the data field to the client only at the time of GET object.
- Or consider saving the data in the data field as a "file" and associating it in the table through Pointer.
- If the data is a huge object and you only need to get one or a few attributes, you can consider specifying the attribute(s) with a dot in select, see Use dot in querying objects.
File storage
Is File Storage CDN-accelerated?
The file storage service of China node comes with CDN acceleration, but it does not include overseas CDN acceleration.
Commercial application can send a work order to request to enable overseas CDN acceleration (after enabling, the cost of http/https traffic for accessing files from overseas will be adjusted to RMB 0.40/GB and RMB 0.60/GB respectively).There is no ready-made CDN acceleration service in the international version, so users need to configure it by themselves.
Take CloudFront acceleration service as an example, the configuration process is as follows:
- Read the official guide Getting Started with CloudFront.
- Create an AWS account to start using and paying for the CloudFront service.
- Public access to S3 (read permission) is already configured, and you can skip the section on S3 configuration in the guide. GettingStarted.html#GettingStartedUploadContent).
- The Origin Domain Name in the CloudFront configuration should be obtained from the URL of the AVFile, all others can be left as default.
Is there a size limit for file storage?
No, there is not.
Except for uploading files through the JavaScript SDK in the browser, or uploading files directly through our website, which has a size limit of 10 MB, there are no restrictions on other SDKs. The JavaScript SDK also has no size limit in the Node.js environment.
Can I store images as thumbnails, etc.?
Yes. By default, our AVFile class provides a way to get thumbnails, see the developer's guide for each SDK. If you want to do it yourself, you can get the URL property of AVFile.
Use Seven Bulls Image Processing API to perform processing, such as adding watermarks, cropping, and so on.
Does file storage support access control?
Since any user who knows the file URL can access the file, you need to set appropriate Class permissions and ACLs for the _File Class and the Class that references the file to restrict unauthorized users from getting to the file URL.
If you want to have more granular control over file access, such as rechecking whether you have access to a file after a certain period of time, it is recommended that you use a third-party file storage provider that supports access rights control, and then save an external URL directly in the LeanCloud File Service.
Note that the _File table is immutable, which means that a URL that has been written cannot be modified.
However, usually file storage providers that support access control implement access rights by passing an additional token parameter (which is usually time-sensitive) after an existing URL, such as https://file.example.com/some-url, for example https://file.example.com/some-url?token=xxxxxx.
So when a client needs to access a file, it can get the url attribute from LCFile and then add this token parameter to form the final URL to download the file.
To get the token, you need to deploy a simple API service that generates the token for accessing the token on the cloud engine or your own server, and the client accesses the API service to get the token.
How do I modify an existing file in the File Store?
The _File class of the file store is immutable data. Once written, the contents of the file and related metadata cannot be modified, but can only be deleted and re-uploaded or rebuilt via URL.
If you are using an external file (constructed via URL) and need to modify the file or metadata frequently, you can consider the following solutions:
- Implement a Class to store information related to external file, such as
ExternalFile. Set a Pointer field in the object that references the file to point toExternalFile. Note that in this case, when querying the object containing the file, if you want to get the file information at the same time, you need to include the corresponding field (if you use the built-in_FileClass, it will be included automatically, no additional specification is required). - In the object that needs to reference the file, you can directly use the string type to save the URL. In this case, file-related functions shoule be implemented by yourself. If you want to save meta information about the file, you need to design it separately. If you want to save the meta information about the file, you need to design it differently, for example, by saving it on other fields of the object, or by changing the type of the corresponding field from string to object and saving both the URL and the meta information. Note that such a design will result in the application's file information being scattered among the classes that need to use the file, and it will be troublesome to batch query and batch process the entire application's files.
SDK
The Size of the iOS Project After Packaging
Create a new blank project and use CocoaPod to install AVOSCloud and AVOSCloudIM modules. At this time, the project size exceeds 80 MB. Will the size shrink after packaging? Approximately how big will it be?
The datastore iOS SDK binary contains 5 CPU slices, including i386, armv7, arm64, etc. Non-ARM symbols and symbols not involved in the connection are stripped out during the release process. Therefore, the final application size will not increase by more than 10 MB, so please feel free to use it.
Why does the Java SDK return null when using the getDate("createdAt") method to read the creation time of an AVObject object?
Use the getCreatedAt method of AVObject; for updatedAt use getUpdatedAt.
Both methods return the Date type.
If you want to return a string, you can use getUpdatedAtString() and getCreatedAtString().
Why does the installationId always change every time an Android device starts up? How can I stop it from changing?
There are two possible reasons for this:
- The SDK version is too old, and the logic for generating the installationId has been modified during version changes. Please update to the latest version.
- Caused by code obfuscation, please add SDK obfuscation exclusion to the proguard file.
How to do Android code obfuscation
Refer to the Android Code Obfuscation documentation.
What is the reason for the error 'already has one request sending' in Java SDK?
The com.avos.avoscloud.AVException: already has one request sending error in the logs indicates that two asynchronous save operations have been performed on the same AVObject instance object at the same time. To prevent data mismatch, the datastore SDK limits such concurrent writes to the same data, so this exception is thrown.
You need to inspect the code and print logs and breakpoints to find out which save line triggered it.
Using the data storage function of the Android SDK, the app was detected by the developer to have a self-start issue when it was uploaded.
Solution: Upgrade the Android SDK to v8.2.19 or above.
The reason for the self-start issue is that LiveQuery needs a long link in the background so that it can receive event notifications from the cloud in time. This long link is placed in a background Service with auto-reconnect capability - it will monitor the network and start this service when the network is active. This logic may be judged as "self-starting" by some platforms.
Older versions of the SDK sometimes threw exceptions because they didn't adapt to the newer versions of Android. The 8.2.19 version of the SDK has adapted to the newer versions of Android, but it doesn't completely prohibit this auto-reconnect logic, so it may still be misjudged. If you have already used the new SDK but still encounter this problem, you can complain to the vendor.
Does JavaScript SDK have a synchronization API?
The JavaScript SDK does not provide a synchronization API due to platform specificity (running in a single-threaded browser or Node.js environment). All APIs that require network interaction need to be called in the form of callbacks. We provide Promise mode to minimize the problem of over-nested callbacks.
JavaScript SDK uses Master Key in AV.init, but the AJAX requests sent returns 206
Currently the JavaScript SDK does not send a Master Key when working in the browser (not Node) because we discourage the use of Master Keys in the browser, which represent the highest level of access to the data and should only be used in backend applications.
If your application is indeed internal (with security measures in place so that it cannot be accessed from the outside), you can add the following code after AV.init to make the JavaScript SDK send the Master Key:
AV.Cloud.useMasterKey(true);
JavaScript SDK will expose App Key and App Id, how to ensure security?
First of all, please read Security overview to understand the complete security system of data storage service. It is mentioned that you can use a "secure domain name", and in the absence of a domain name, you can use ACL.
Theoretically all clients are untrusted, so security needs to be designed on the server side. If you need advanced security, you can use the ACL management. If you need more advanced customization, you can use the cloud engine.
Other
How to prevent DDoS attacks, or high-frequency CC attacks?
Whether it is a DDoS attack or a high-frequency CC attack, it is necessary to set up a high-defense resource in front of the independent IP requested by the service. The specific steps are as follows:
- Bind a domain name that has been filed in the console. To use data storage and instant messaging services, you need to bind the API domain name, and to use cloud engine services, you need to bind the domain name of the cloud engine. when the SDK is initialized, specify the Server URL as the address of the API domain name bound to the console. To bind a domain name, go to Console > Application > Settings > Domain Binding.
- Set the DNS resolution to a separate IP (set the IP address to an A record) when binding the domain name. Independent IP can be viewed at Console Personal Center > Account Settings > Independent IP, API and Cloud Engine have different IPs, one API independent IP is free for Commercial Edition users, and the second API independent IP is charged from the moment you purchase it, there is no free IP for Cloud Engine, each IP is charged at $50 per month. 3. Purchase high security resources from a third party.
- Purchase high defense resources from a third party and use the newly purchased IPs above to round-trip to the source.
Since many network attacks are destined to specific IPs, if the standalone IP is already publicly available with the service, you can purchase another standalone IP to be the source IP of the high defense resource to avoid the high defense resource failing due to the unavailability of the source IP.
Saving data gives an error ‘The key is too long’, what is the problem?
You can check whether the field you want to save or update is indexed or not. The length limit of indexed field cannot exceed 1 KB.
How to address data consistency or transaction needs?
The data storage service does not provide complete transaction function at present, but it provides some features to ensure data consistency, which can solve most of the consistency needs:
- Updates to multiple fields are done atomically in a single save operation on a single object.
- Numeric fields can be updated atomically using increment (atomic counter).
- Unique-index ensures that there is only one object with the same value on a field.
- Conditional update object can be updated only when a certain query condition is met; based on this feature, you can implement a more complex two-phase commit.
- You can also implement custom exclusion locks on the cloud engine with the help of LeanCache. functions/redlock.js).
We've also recorded a public video on this topic, which includes a detailed introduction to the above features and practical tutorials for solving common scenarios (including implementing a two-stage submission).